Computer engineering (CE, CoE, or CpE) is a branch of
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
specialized in developing
computer hardware
Computer hardware includes the physical parts of a computer, such as the central processing unit (CPU), random-access memory (RAM), motherboard, computer data storage, graphics card, sound card, and computer case. It includes external devices ...
and
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
.
It integrates several fields of
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
,
electronics engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flow ...
and
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
.
Computer engineering is referred to as ''electrical and computer engineering'' or ''
computer science and engineering
Computer science and engineering (CSE) is an academic subject comprising approaches of computer science and computer engineering. There is no clear division in computing between science and engineering, just like in the field of materials science ...
'' at some universities.
Computer engineers require training in hardware-software integration,
software design
Software design is the process of conceptualizing how a software system will work before it is implemented or modified.
Software design also refers to the direct result of the design process the concepts of how the software will work which co ...
, and
software engineering
Software engineering is a branch of both computer science and engineering focused on designing, developing, testing, and maintaining Application software, software applications. It involves applying engineering design process, engineering principl ...
. It can encompass areas such as
electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
,
artificial intelligence (AI),
robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
,
computer networks
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or ...
,
computer architecture and
operating systems
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, from the design of individual
microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
s,
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
s,
personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s, and
supercomputer
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instruc ...
s, to
circuit design
In electrical engineering, the process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a pl ...
. This field of engineering not only focuses on how computer systems themselves work, but also on how to integrate them into the larger picture.
Robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
are one of the applications of computer engineering.
Computer engineering usually deals with areas including
writing software and
firmware
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, h ...
for
embedded microcontroller
A microcontroller (MC, uC, or μC) or microcontroller unit (MCU) is a small computer on a single integrated circuit. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable input/output peripherals. Pro ...
s, designing
VLSI chips
''CHiPs'' is an American crime drama television series created by Rick Rosner and originally aired on NBC from September 15, 1977, to May 1, 1983. After the final first-run telecast on NBC in May 1983, the series went into reruns on Sundays fr ...
,
analog sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
s,
mixed signal circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a laminated sandwich structure of conductive and insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes and other features (similar to wires on a flat surface) ...
s,
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, Work (thermodynamics), work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed b ...
and
Control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s. Computer engineers are also suited for
robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
research, which relies heavily on using
digital systems
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical signals through ...
to control and monitor
electrical systems
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
like
motor
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.
Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power gene ...
s,
communications
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not onl ...
, and
sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
s.
In many institutions of higher learning, computer engineering students are allowed to choose areas of in-depth study in their junior and senior years because the full breadth of knowledge used in the design and application of computers is beyond the scope of an
undergraduate degree
An undergraduate degree (also called first degree or simply degree) is a colloquial term for an academic degree earned by a person who has completed undergraduate courses. In the United States, it is usually offered at an institution of higher ed ...
. Other institutions may require
engineering students to complete one or two years of
general engineering before declaring computer engineering as their primary focus.

History
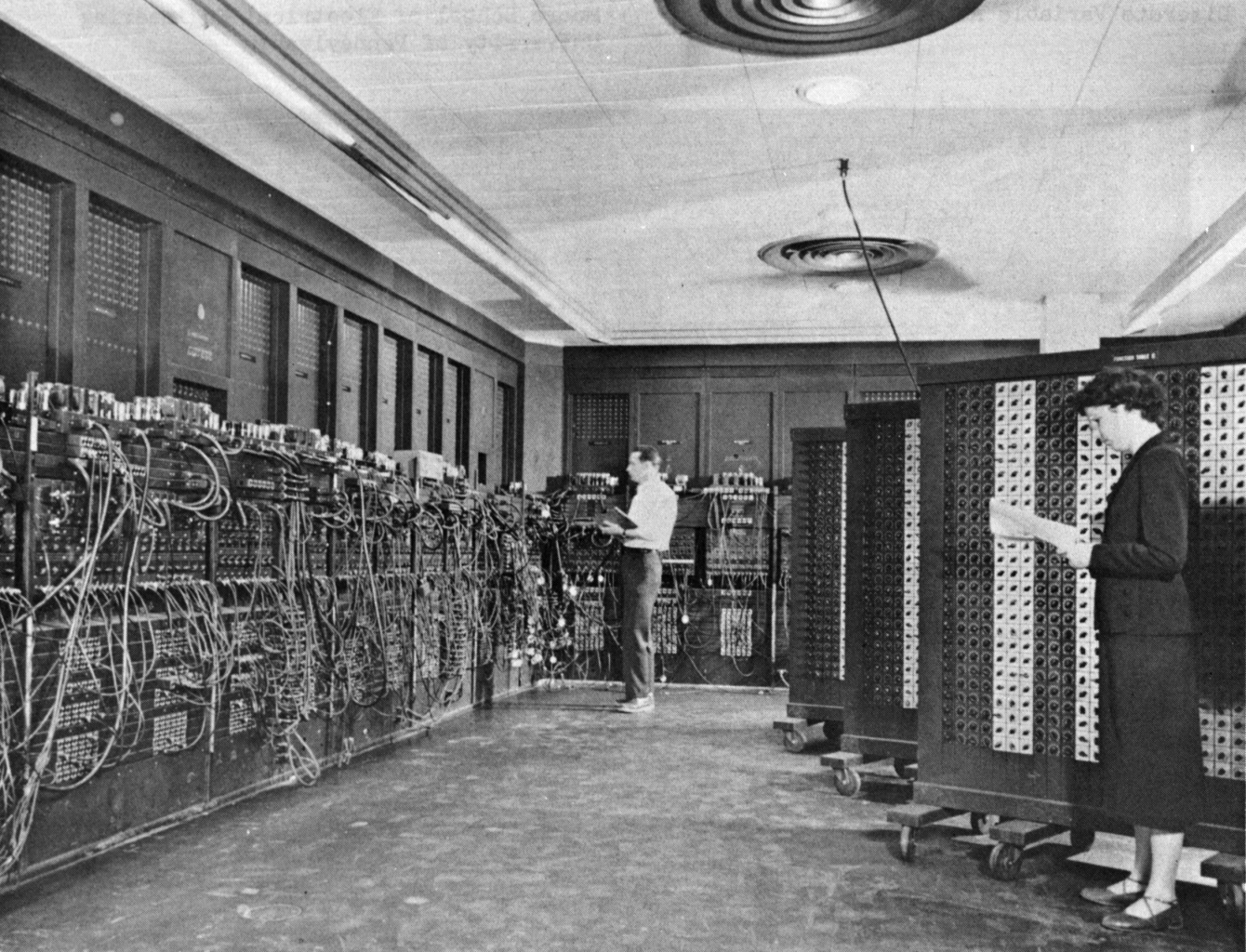

Computer engineering began in 1939 when
John Vincent Atanasoff
John Vincent Atanasoff (October 4, 1903 – June 15, 1995) was an American physicist and inventor credited with inventing the first electronic digital computer. Atanasoff invented the first electronic digital computer in the 1930s at Iowa Stat ...
and
Clifford Berry
Clifford Edward Berry (April 19, 1918 – October 30, 1963) was an American computer scientist who helped John Vincent Atanasoff
John Vincent Atanasoff (October 4, 1903 – June 15, 1995) was an American physicist and inventor credited wi ...
began developing the world's first electronic
digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', wh ...
through
physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
,
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, and
electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
. John Vincent Atanasoff was once a physics and mathematics teacher for
Iowa State University
Iowa State University of Science and Technology (Iowa State University, Iowa State, or ISU) is a Public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Ames, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1858 as the Iowa Agricult ...
and Clifford Berry a former graduate under electrical engineering and physics. Together, they created the
Atanasoff-Berry computer, also known as the ABC which took five years to complete.
While the original ABC was dismantled and discarded in the 1940s, a tribute was made to the late inventors; a replica of the ABC was made in 1997, where it took a team of researchers and engineers four years and $350,000 to build.
The modern
personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
emerged in the 1970s, after several breakthroughs in
semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
technology. These include the first working
transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
by
William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley ( ; February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American solid-state physicist, electrical engineer, and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brat ...
,
John Bardeen
John Bardeen (; May 23, 1908 – January 30, 1991) was an American solid-state physicist. He is the only person to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics twice: first in 1956 with William Shockley and Walter Houser Brattain for their inventio ...
and
Walter Brattain
Walter Houser Brattain (; February 10, 1902 – October 13, 1987) was an American solid-state physicist who shared the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics with John Bardeen and William Shockley for their invention of the point-contact transistor. Bratt ...
at
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
in 1947, in 1955, silicon dioxide surface passivation by
Carl Frosch
Carl John Frosch (September 6, 1908 – May 18, 1984) was a Bell Labs researcher. With Lincoln Derrick, Lincoln Derick, Frosch discovered that silicon could be protectively coated by silicon dioxide by the right exposure to oxygen when hot, and ...
and Lincoln Derick, the first planar silicon dioxide transistors by Frosch and Derick in 1957,
planar process
The planar process is a semiconductor device fabrication, manufacturing process used in the semiconductor industry to build individual components of a transistor, and in turn, connect those transistors together. It is the primary process by which ...
by
Jean Hoerni
Jean Amédée Hoerni (September 26, 1924 – January 12, 1997) was a Swiss-born American engineer. He was a silicon transistor pioneer, and a member of the "traitorous eight". He developed the planar process, an important technology for reliably ...
,
the
monolithic integrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
chip by
Robert Noyce
Robert Norton Noyce (December 12, 1927 – June 3, 1990), nicknamed "the Mayor of Silicon Valley", was an American physicist and entrepreneur who co-founded Fairchild Semiconductor in 1957 and Intel Corporation in 1968. He was also credited w ...
at
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument by the " traitorous eight" who defected from Shockley Semi ...
in 1959,
the
metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor
upright=1.3, Two power MOSFETs in amperes">A in the ''on'' state, dissipating up to about 100 watt">W and controlling a load of over 2000 W. A matchstick is pictured for scale.
In electronics, the metal–oxide–semiconductor field- ...
(MOSFET, or MOS transistor) demonstrated by a team at Bell Labs in 1960 and the single-chip
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
(
Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 was part of the 4 chip MCS-4 micro computer set, released by the Intel, Intel Corporation in November 1971; the 4004 being part of the first commercially marketed microprocessor chipset, and the first in a long line of List of I ...
) by
Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin (, ; born 1 December 1941) is an Italian-American physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the desig ...
,
Marcian Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937, in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic In ...
,
Masatoshi Shima and
Stanley Mazor at
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and Delaware General Corporation Law, incorporated in Delaware. Intel designs, manufactures, and sells computer compo ...
in 1971.
History of computer engineering education
The first computer engineering degree program in the United States was established in 1971 at
Case Western Reserve University
Case Western Reserve University (CWRU) is a Private university, private research university in Cleveland, Ohio, United States. It was established in 1967 by a merger between Western Reserve University and the Case Institute of Technology. Case ...
in
Cleveland
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–U.S. maritime border and approximately west of the Ohio-Pennsylvania st ...
,
Ohio
Ohio ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the ...
. , there were 250
ABET
ABET (pronounced A-bet), formerly known as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., is a non-governmental accreditation organization for post-secondary programs in engineering, engineering technology, computing, and applied ...
-accredited computer engineering programs in the U.S. In Europe, accreditation of computer engineering schools is done by a variety of agencies as part of the
EQANIE
EQANIE (European Quality Assurance Network for Informatics Education e.V.) is a non-profit association seeking to enhance evaluation and quality assurance of Informatics (academic field), informatics study programmes and education in Europe. It was ...
network. Due to increasing job requirements for engineers who can concurrently design hardware,
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, firmware, and manage all forms of computer systems used in industry, some tertiary institutions around the world offer a
bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Medieval Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to six years ...
generally called computer engineering. Both computer engineering and
electronic engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flo ...
programs include analog and digital circuit design in their curriculum. As with most engineering disciplines, having a sound knowledge of
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
and science is necessary for computer engineers.
Education
Computer engineering is referred to as
computer science and engineering
Computer science and engineering (CSE) is an academic subject comprising approaches of computer science and computer engineering. There is no clear division in computing between science and engineering, just like in the field of materials science ...
at some universities. Most entry-level computer engineering jobs require at least a bachelor's degree in computer engineering, electrical engineering or computer science. Typically one must learn an array of
mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
such as
calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
,
linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
and
differential equations, along with
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
. Degrees in
electronic or
electric engineering also suffice due to the similarity of the two fields. Because hardware engineers commonly work with computer software systems, a strong background in computer programming is necessary. According to BLS, "''a computer engineering major is similar to electrical engineering but with some computer science courses added to the curriculum''".
Some large firms or specialized jobs require a master's degree.
It is also important for computer engineers to keep up with rapid advances in
technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
. Therefore, many continue learning throughout their careers. This can be helpful, especially when it comes to learning new skills or improving existing ones. For example, as the relative cost of fixing a
bug increases the further along it is in the software development cycle, there can be greater cost savings attributed to developing and testing for quality code as soon as possible in the process, particularly before release.
Professions
A person with a profession in computer engineering is called a computer engineer.
Applications and practice
There are two major focuses in computer engineering: hardware and software.
Computer hardware engineering
According to the United States
BLS, job outlook employment for computer hardware engineers, the expected ten-year growth from 2019 to 2029 for computer hardware engineering was an estimated 2% and a total of 71,100 jobs. ("''Slower than average''" in their own words when compared to other occupations)".
This is a decrease from the 2014 to 2024 BLS computer hardware engineering estimate of 3% and a total of 77,700 jobs; "''and is down from 7% for the 2012 to 2022 BLS estimate and is further down from 9% in the BLS 2010 to 2020 estimate.''"
Today, computer hardware is somewhat equal to electronic and computer engineering (ECE) and has been divided into many subcategories, the most significant being
embedded system design.
Computer software engineering
According to the U.S.
Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) is a unit of the United States Department of Labor. It is the principal fact-finding agency for the government of the United States, U.S. government in the broad field of labor economics, labor economics and ...
(BLS), "''computer applications software engineers and computer systems software engineers are projected to be among the faster than average growing occupations''" The expected ten-year growth for computer software engineering was an estimated seventeen percent and there was a total of 1,114,000 jobs that same year.
This is down from the 2012 to 2022 BLS estimate of 22% for software developers.
And, further down from the 30% 2010 to 2020 BLS estimate.
In addition, growing concerns over cybersecurity add up to put computer software engineering high above the average rate of increase for all fields. However, some of the work will be outsourced in foreign countries. Due to this, job growth will not be as fast as during the last decade, as jobs that would have gone to computer software engineers in the United States would instead go to computer software engineers in countries such as India.
In addition, the BLS job outlook for Computer Programmers, 2014–24 has an −8% (a decline, in their words),
then a job outlook, 2019-29 of -9% (Decline),
then a 10% decline for 2021-2031
and now an 11% decline for 2022-2032
for those who program computers (i.e. embedded systems) who are not computer application developers. Furthermore, women in software fields has been declining over the years even faster than other engineering fields.
Specialty areas
There are many specialty areas in the field of computer engineering.
Processor design
Processor design process involves choosing an
instruction set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA) is an abstract model that generally defines how software controls the CPU in a computer or a family of computers. A device or program that executes instructions described by that ISA, s ...
and a certain execution paradigm (e.g.
VLIW
Very long instruction word (VLIW) refers to instruction set architectures that are designed to exploit instruction-level parallelism (ILP). A VLIW processor allows programs to explicitly specify instructions to execute in parallel computing, para ...
or
RISC
In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a comp ...
) and results in a
microarchitecture
In electronics, computer science and computer engineering, microarchitecture, also called computer organization and sometimes abbreviated as μarch or uarch, is the way a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented in a particular ...
, which might be described in e.g.
VHDL
VHDL (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit Program, VHSIC Hardware Description Language) is a hardware description language that can model the behavior and structure of Digital electronics, digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ran ...
or
Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits, with the highest level of abstraction being at the re ...
.
CPU design is divided into design of the following components:
datapaths (such as
ALUs and
pipelines
A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The Un ...
), control unit: logic which controls the datapaths,
memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembe ...
components such as
register files,
caches, clock circuitry such as clock drivers, PLLs, clock distribution networks, pad transceiver circuitry, logic gate cell library which is used to implement the logic.
Coding, cryptography, and information protection
Computer engineers work in coding, applied cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as
digital images
A digital image is an image composed of picture elements, also known as pixels, each with '' finite'', '' discrete quantities'' of numeric representation for its intensity or gray level that is an output from its two-dimensional functions f ...
and
music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
, fragmentation,
copyright infringement
Copyright infringement (at times referred to as piracy) is the use of Copyright#Scope, works protected by copyright without permission for a usage where such permission is required, thereby infringing certain exclusive rights granted to the c ...
and other forms of tampering by, for example,
digital watermarking
A digital watermark is a kind of marker covertly embedded in a noise-tolerant signal such as audio, video or image data.H.T. Sencar, M. Ramkumar and A.N. Akansu: ''Data Hiding Fundamentals and Applications: Content Security in Digital Multimedia'' ...
.
Communications and wireless networks
Those focusing on communications and wireless networks, work advancements in telecommunications systems and networks (especially wireless networks), modulation and error-control coding, and information theory. High-speed
network design
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics
...
, interference suppression and modulation, design, and analysis of
fault-tolerant system
Fault tolerance is the ability of a system to maintain proper operation despite failures or faults in one or more of its components. This capability is essential for high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems.
Fault to ...
, and storage and transmission schemes are all a part of this specialty.
Compilers and operating systems

This specialty focuses on
compiler
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primaril ...
s and
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s design and development. Engineers in this field develop new operating system architecture, program analysis techniques, and new techniques to assure quality. Examples of work in this field include post-link-time code transformation
algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algo ...
development and new operating system development.
Computational science and engineering
Computational science and engineering is a relatively new discipline. According to the Sloan Career Cornerstone Center, individuals working in this area, "''computational methods are applied to formulate and solve complex mathematical problems in engineering and the physical and the social sciences. Examples include aircraft design, the plasma processing of nanometer features on semiconductor wafers,
VLSI circuit design, radar detection systems, ion transport through biological channels, and much more''".
Computer networks, mobile computing, and distributed systems
In this specialty, engineers build integrated environments for computing, communications, and
information access
Information access is the freedom or ability to identify, obtain and make use of database or information effectively.
There are various research efforts in information access for which the objective is to simplify and make it more effective fo ...
. Examples include shared-channel wireless networks,
adaptive resource management in various systems, and improving the quality of service in
mobile and ATM environments. Some other examples include work on
wireless network systems and fast
Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
cluster wired systems.
Computer systems: architecture, parallel processing, and dependability

Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for
multithreading and
parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories,
algorithms
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for per ...
, and other tools that add
performance
A performance is an act or process of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Performance has evolved glo ...
to computer systems.
Computer architecture includes
CPU design
Processor design is a subfield of computer science and computer engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor (computing), processor, a key component of computer hardware.
The design process involves choosing an instruction set an ...
,
cache hierarchy
Cache hierarchy, or multi-level cache, is a memory architecture that uses a hierarchy of memory stores based on varying access speeds to cache data. Highly requested data is cached in high-speed access memory stores, allowing swifter access by cent ...
layout,
memory organization, and
load balancing.
Computer vision and robotics
In this specialty, computer engineers focus on developing
visual sensing technology to sense an environment, representation of an environment, and manipulation of the environment. The gathered three-dimensional information is then implemented to perform a variety of tasks. These include improved human modeling, image communication, and human-computer interfaces, as well as devices such as special-purpose cameras with versatile vision sensors.
Embedded systems
Individuals working in this area design technology for enhancing the speed, reliability, and performance of systems. Embedded systems are found in many devices from a small
FM radio
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting that uses frequency modulation (FM) of the radio broadcast carrier wave. Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to transmit high fidelity, high-f ...
to the space shuttle. According to the Sloan Cornerstone Career Center, ongoing developments in embedded systems include "''automated vehicles and equipment to conduct search and rescue, automated transportation systems, and human-robot coordination to repair equipment in space.''"
, computer embedded systems specializations include
system-on-chip
A system on a chip (SoC) is an integrated circuit that combines most or all key components of a computer or electronic system onto a single microchip. Typically, an SoC includes a central processing unit (CPU) with memory, input/output, and da ...
design, the architecture of
edge computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. More broadly, it refers to any design that pushes computation physically closer to a user, so as to reduce the Latency (engineer ...
and the
Internet of things
Internet of things (IoT) describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the Internet or other communication networks. The IoT encompasse ...
.
Integrated circuits, VLSI design, testing and CAD
This specialty of computer engineering requires adequate knowledge of electronics and electrical systems. Engineers working in this area work on enhancing the speed, reliability, and energy efficiency of next-generation very-large-scale integrated (
VLSI) circuits and microsystems. An example of this specialty is work done on reducing the power consumption of VLSI algorithms and architecture.
Signal, image and speech processing
Computer engineers in this area develop improvements in human–computer interaction, including
speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
and synthesis, medical and scientific imaging, or communications systems. Other work in this area includes computer vision development such as
recognition of human facial features.
Quantum computing
This area integrates the
quantum
In physics, a quantum (: quanta) is the minimum amount of any physical entity (physical property) involved in an interaction. The fundamental notion that a property can be "quantized" is referred to as "the hypothesis of quantization". This me ...
behaviour of small particles such as
superposition
In mathematics, a linear combination or superposition is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results (e.g. a linear combination of ''x'' and ''y'' would be any expression of the form ...
,
interference
Interference is the act of interfering, invading, or poaching. Interference may also refer to:
Communications
* Interference (communication), anything which alters, modifies, or disrupts a message
* Adjacent-channel interference, caused by extra ...
and
entanglement, with classical computers to solve complex problems and formulate algorithms much more efficiently. Individuals focus on fields like
Quantum cryptography
Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution, which offers an information-theoretically secure soluti ...
,
physical simulations and
quantum algorithms
In quantum computing, a quantum algorithm is an algorithm that runs on a realistic model of quantum computation, the most commonly used model being the quantum circuit model of computation. A classical (or non-quantum) algorithm is a finite sequ ...
.
Benefits of Engineering in Society
An accessible avenue for obtaining information and opportunities in technology, especially for young students, is through digital platforms, enabling learning, exploration, and potential income generation at minimal cost and in regional languages, none of which would be possible without engineers. Computer engineering is important in the changes involved in industry 4.0, with engineers responsible for designing and optimizing the technology that surrounds our lives, from
big data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with ...
to
AI. Their work not only facilitates global connections and knowledge access, but also plays a pivotal role in shaping our future, as technology continues to evolve rapidly, leading to a growing demand for skilled computer engineers. Engineering contributes to improving society by creating devices and structures impacting various aspects of our lives, from technology to infrastructure. Engineers also address challenges such as
environmental protection
Environmental protection, or environment protection, refers to the taking of measures to protecting the natural environment, prevent pollution and maintain ecological balance. Action may be taken by individuals, advocacy groups and governments. ...
and
sustainable development
Sustainable development is an approach to growth and Human development (economics), human development that aims to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.United Nations General ...
, while developing medical treatments. As of 2016, the median annual wage across all BLS engineering categories was over $91,000. Some were much higher, with engineers working for petroleum companies at the top (over $128,000). Other top jobs include: Computer Hardware Engineer – $115,080, Aerospace Engineer – $109,650, Nuclear Engineer – $102,220.
See also
Related fields
Associations
*
IEEE Computer Society
IEEE Computer Society (commonly known as the Computer Society or CS) is a technical society of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) dedicated to computing, namely the major areas of hardware, software, standards and people ...
*
Association for Computing Machinery
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) is a US-based international learned society for computing. It was founded in 1947 and is the world's largest scientific and educational computing society. The ACM is a non-profit professional membe ...
*
British Computer Society
image:Maurice Vincent Wilkes 1980 (3).jpg, Sir Maurice Wilkes served as the first President of BCS in 1957.
The British Computer Society (BCS), branded BCS, The Chartered Institute for IT, since 2009, is a professional body and a learned ...
Notes and references
Notes
References
External links
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Computer Engineering
Electrical and computer engineering
Engineering disciplines


 Computer engineering began in 1939 when
Computer engineering began in 1939 when  Computer engineers work in coding, applied cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as
Computer engineers work in coding, applied cryptography, and information protection to develop new methods for protecting various information, such as  This specialty focuses on
This specialty focuses on  Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multithreading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories,
Engineers working in computer systems work on research projects that allow for reliable, secure, and high-performance computer systems. Projects such as designing processors for multithreading and parallel processing are included in this field. Other examples of work in this field include the development of new theories,